Every app needs authentication and authorization. Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the SAML sign-in experience (user authentication) with Python and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of Python.
- A usable SAML account.
Create an application in Logto
In you browser, open a new tab and enter the link of Logto Admin Console.
Once the page is loaded, in the "Get Started" section click the View all link to open the application framework list page.
Choose your application type
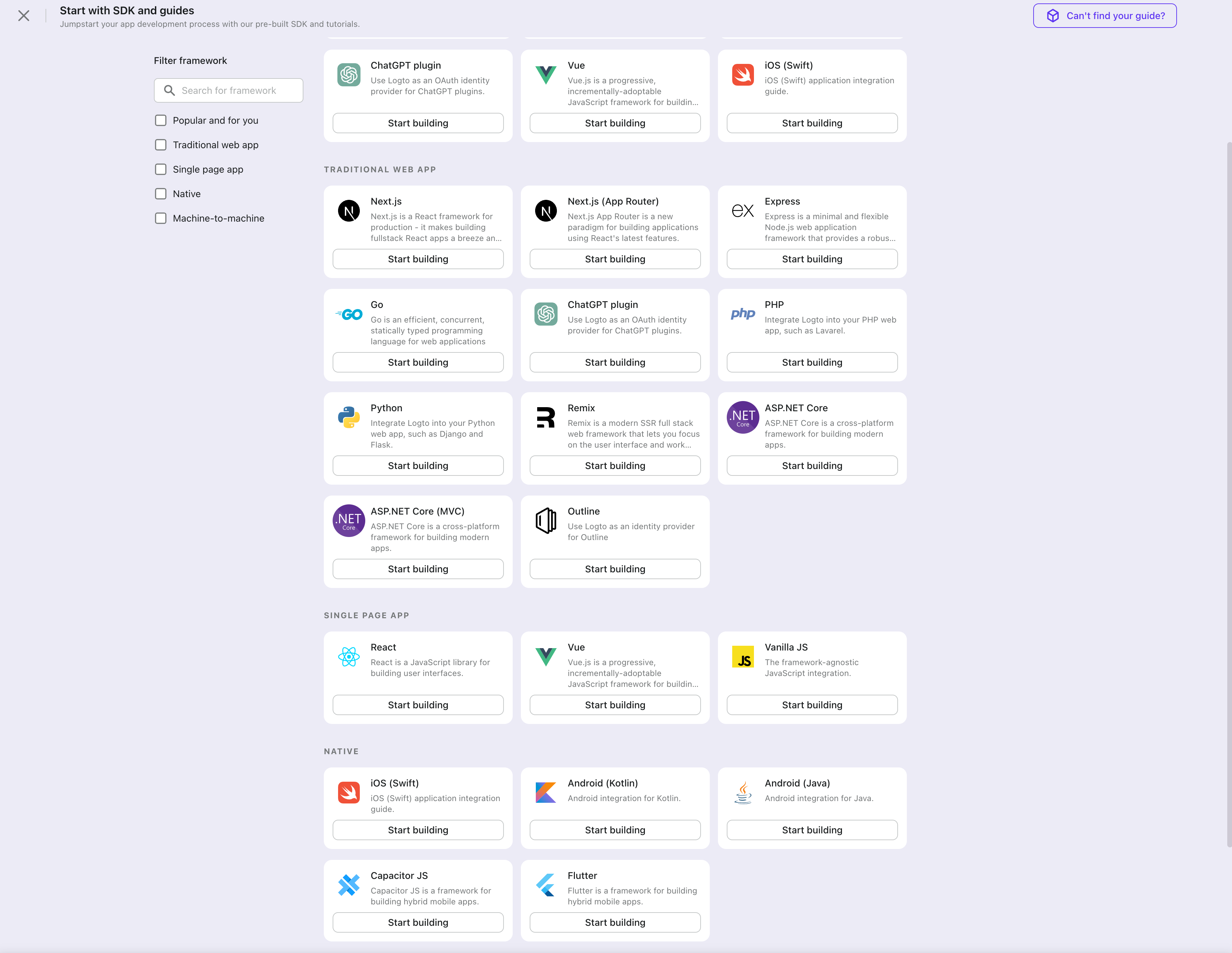
In the opening modal, scroll to the "Traditional web" section or filter all the available " Traditional web" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left.
Click the "Flask" framework card to start creating your application.
Enter application name
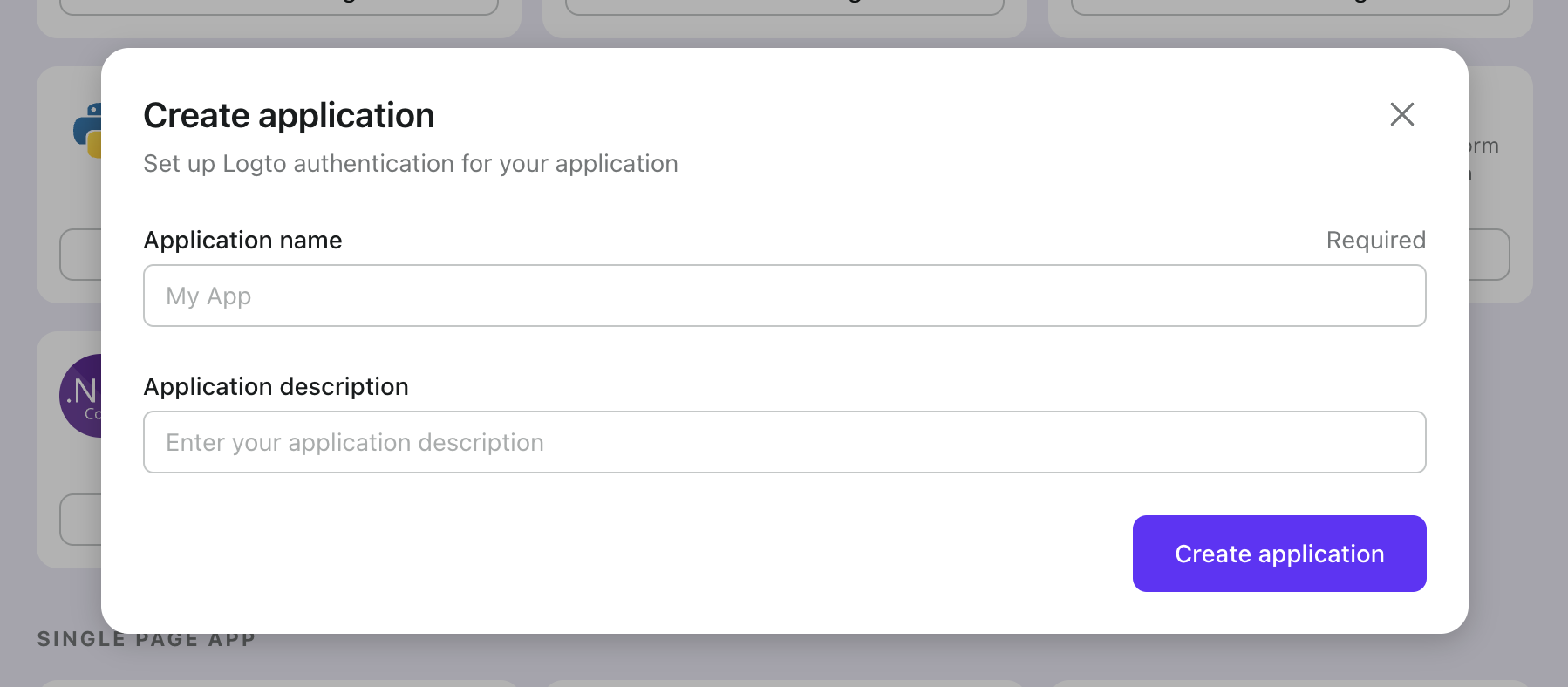
Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application."
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate Logto SDK
- The example uses Flask, but the concepts are the same for other frameworks.
- The Python sample project is available on our Python SDK repo.
- Logto SDK leverages coroutines, remember to use
awaitwhen calling async functions.
Installation
Execute in the project root directory:
pip install logto # or `poetry add logto` or whatever you use
Init LogtoClient
First, create a Logto config:
from logto import LogtoClient, LogtoConfig
client = LogtoClient(
LogtoConfig(
endpoint="https://you-logto-endpoint.app", # Replace with your Logto endpoint
appId="replace-with-your-app-id",
appSecret="replace-with-your-app-secret",
),
)
You can find and copy "App Secret" from application details page in Admin Console:
Also replace the default memory storage with a persistent storage, for example:
from logto import LogtoClient, LogtoConfig, Storage
from flask import session
from typing import Union
class SessionStorage(Storage):
def get(self, key: str) -> Union[str, None]:
return session.get(key, None)
def set(self, key: str, value: Union[str, None]) -> None:
session[key] = value
def delete(self, key: str) -> None:
session.pop(key, None)
client = LogtoClient(
LogtoConfig(...),
storage=SessionStorage(),
)
See Storage for more details.
Implement sign-in and sign-out
In your web application, add a route to properly handle the sign-in request from users. Let's use /sign-in as an example:
@app.route("/sign-in")
async def sign_in():
# Get the sign-in URL and redirect the user to it
return redirect(await client.signIn(
redirectUri="http://localhost:3000/callback",
))
Replace http://localhost:3000/callback with the callback URL you set in your Logto Console for this application.
If you want to show the sign-up page on the first screen, you can set interactionMode to signUp:
@app.route("/sign-in")
async def sign_in():
return redirect(await client.signIn(
redirectUri="http://localhost:3000/callback",
interactionMode="signUp", # Show the sign-up page on the first screen
))
Now, whenever your users visit http://localhost:3000/sign-in, it will start a new sign-in attempt and redirect the user to the Logto sign-in page.
Note Creating a sign-in route isn't the only way to start a sign-in attempt. You can always use the
signInmethod to get the sign-in URL and redirect the user to it.
After the user makes a signing-out request, Logto will clear all user authentication information in the session.
To clean up the Python session and Logto session, a sign-out route can be implemented as follows:
@app.route("/sign-out")
async def sign_out():
return redirect(
# Redirect the user to the home page after a successful sign-out
await client.signOut(postLogoutRedirectUri="http://localhost:3000/")
)
Handle authentication status
In Logto SDK, we can use client.isAuthenticated() to check the authentication status, if the user is signed in, the value will be true, otherwise, the value will be false.
Here we also implement a simple home page for demonstration:
- If the user is not signed in, show a sign-in button;
- If the user is signed in, show a sign-out button.
@app.route("/")
async def home():
if client.isAuthenticated() is False:
return "Not authenticated <a href='/sign-in'>Sign in</a>"
return "Authenticated <a href='/sign-out'>Sign out</a>"
Open your Python app to test if the integration works. When you click the "Sign In" button, the page should be redirected to a Logto sign-in page, and you should be able to create a new account by entering username and password and complete the sign-in process.
Add SAML connector
To add a social connector, go to the "Connector" tab in the Admin Console, then click on "Social connectors". From there, click "Add social connector".
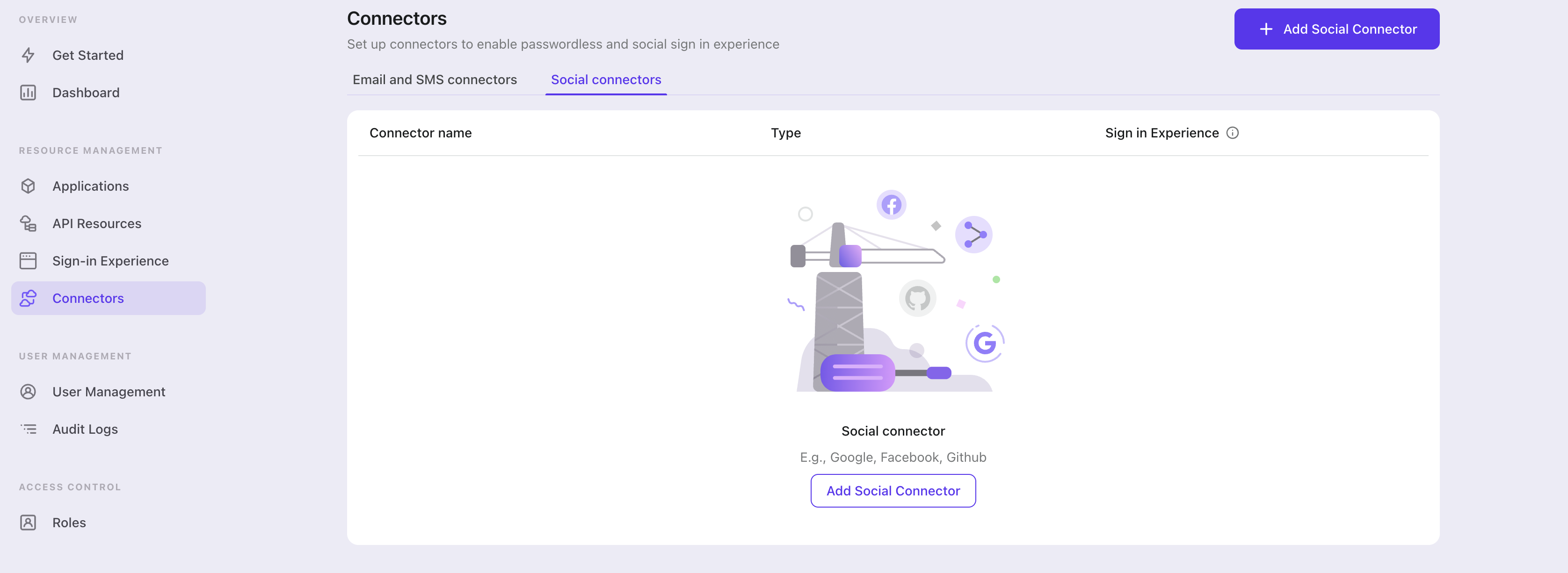
In the openning modal, select "SAML" and click "Next".
On the next page, you will see a two-column layout with the README content on the left and configuration on the right.
Feel free to follow the README file in place or read the following section to complete the configuration process. If you follow the in-place guide, you can skip the next section.
Set up Standard SAML app
Create social IdP's account and register SAML application (IdP)
Let's go through configurations of SAML connector.
Before we kicking off, you can go to a social identity provider which supports SAML protocol and create your own account. Okta, OneLogin, Salesforce and some other platforms support authentication based on SAML protocol.
If your IdP mandate the encryption of SAML assertion and receiving of signed authentication requests, you should generate your private key and corresponding certificate using RSA algorithm. Keep the private key for your SP use and upload the certificate to IdP.
You also need to configure the ACS (Assertion Consumer Service) URL as ${your_logto_origin}/api/authn/saml/${connector_id} to handle IdP's SAML assertion. Where you can find your connectorId at SAML connector's details page in Logto's Admin Console.
ℹ️ Note
Per current Logto's design, we only support Redirect-binding for sending authentication request and POST-binding for receiving SAML assertion. Although this sounds not cool, but we believe that the current design can handle most of your use cases. If you have any problems, feel free to reach out!
Configure SAML connector (SP)
In this section, we will introduce each attribute in detail.
entityID Required
entityID (i.e. issuer) is Entity identifier. It is used to identify your entity (SAML SP entity), and match the equivalence in each SAML request/response.
signInEndpoint Required
The IdP's endpoint that you send SAML authentication requests to. Usually, you can find this value in IdP details page (i.e. IdP's SSO URL or Login URL).
x509Certificate Required
The x509 certificate generated from IdPs private key, IdP is expected to have this value available.
The content of the certificate comes with -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- header and -----END CERTIFICATE----- tail.
idpMetadataXml Required
The field is used to place contents from your IdP metadata XML file.
ℹ️ Note
The XML parser we are using does not support customized namespace. If the IdP metadata comes with namespace, you should manually remove them. For namespace of XML file, see reference.
assertionConsumerServiceUrl Required
The assertion consumer service (ACS) URL is the SP's endpoint to receive IdP's SAML Assertion POST requests. As we mentioned in previous part, it is usually configured at IdP settings but some IdP get this value from SAML authentication requests, we hence also add this value as a REQUIRED field. It's value should look like ${your_logto_origin}/api/authn/saml/${connector_id}.
signAuthnRequest
The boolean value that controls whether SAML authentication request should be signed, whose default value is false.
encryptAssertion
encryptAssertion is a boolean value that indicates if IdP will encrypt SAML assertion, with default value false.
ℹ️ Note
signAuthnRequestandencryptAssertionattributes should align with corresponding parameters of IdP setting, otherwise error will be thrown to show that configuration does not match. All SAML responses need to be signed.
requestSignatureAlgorithm
This should be aligned with the signature algorithms of IdP so that Logto can verify the signature of the SAML assertion. Its value should be either http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1, http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 or http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha512 and the default value is http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256.
messageSigningOrder
messageSigningOrder indicates the signing and encrypting order of IdP, it's value should be either sign-then-encrypt or encrypt-then-sign and the default value is sign-then-encrypt.
privateKey and privateKeyPass
privateKey is an OPTIONAL value and is required when signAuthnRequest is true.
privateKeyPass is the password you've set when creating privateKey, required when necessary.
If signAuthnRequest is true, the corresponding certificate generated from privateKey is required by IdP for checking the signature.
encPrivateKey and encPrivateKeyPass
encPrivateKey is an OPTIONAL value and is required when encryptAssertion is true.
encPrivateKeyPass is the password you've set when creating encPrivateKey, required when necessary.
If encryptAssertion is true, the corresponding certificate generated from encPrivateKey is required by IdP for encrypting SAML assertion.
ℹ️ Note
For keys and certificates generation,
opensslis a wonderful tool. Here is sample command line that might be helpful:openssl genrsa -passout pass:${privateKeyPassword} -out ${encryptPrivateKeyFilename}.pem 4096
openssl req -new -x509 -key ${encryptPrivateKeyFilename}.pem -out ${encryptionCertificateFilename}.cer -days 3650
privateKeyandencPrivateKeyfiles are enforced to be encoded inpkcs1scheme as pem string, which means the private key files should start with-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----and end with-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----.
nameIDFormat
nameIDFormat is an OPTIONAL attribute that declares the name id format that would respond. The value can be among urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:X509SubjectName, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent and urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient, and the default value is urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:unspecified.
timeout
timeout is the time tolerance for time validation, since the time between your SP entity and IdP entity could be different and network connection may also bring some delay. The unit is in millisecond, and the default value is 5000 (i.e. 5s).
profileMap
Logto also provide a profileMap field that users can customize the mapping from the social vendors' profiles which are usually not standard. Each profileMap keys is Logto's standard user profile field name and corresponding value should be social profiles field name. In current stage, Logto only concern 'id', 'name', 'avatar', 'email' and 'phone' from social profile, only 'id' is REQUIRED and others are optional fields.
Config types
| Name | Type | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| signInEndpoint | string | true | |
| x509certificate | string | true | |
| idpMetadataXml | string | true | |
| entityID | string | true | |
| assertionConsumerServiceUrl | string | true | |
| messageSigningOrder | encrypt-then-sign | sign-then-encrypt | false | sign-then-encrypt |
| requestSignatureAlgorithm | http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha512 | false | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 |
| signAuthnRequest | boolean | false | false |
| encryptAssertion | boolean | false | false |
| privateKey | string | false | |
| privateKeyPass | string | false | |
| nameIDFormat | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:X509SubjectName | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient | false | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified |
| timeout | number | false | 5000 |
| profileMap | ProfileMap | false |
| ProfileMap fields | Type | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | false | id |
| name | string | false | name |
| avatar | string | false | avatar |
| string | false | ||
| phone | string | false | phone |
Reference
- Profiles for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0
- samlify - Highly configuarable Node.js SAML 2.0 library for Single Sign On
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the SAML connector should be available now.
Enable SAML connector in Sign-in Experience
Switch to the "Sign-in experience" tab, then click the "Sign-up and sign-in" tab.
If it's the first time you enter the tab, you will see a quick introduction about Sign-in Experience and its basic configuration.
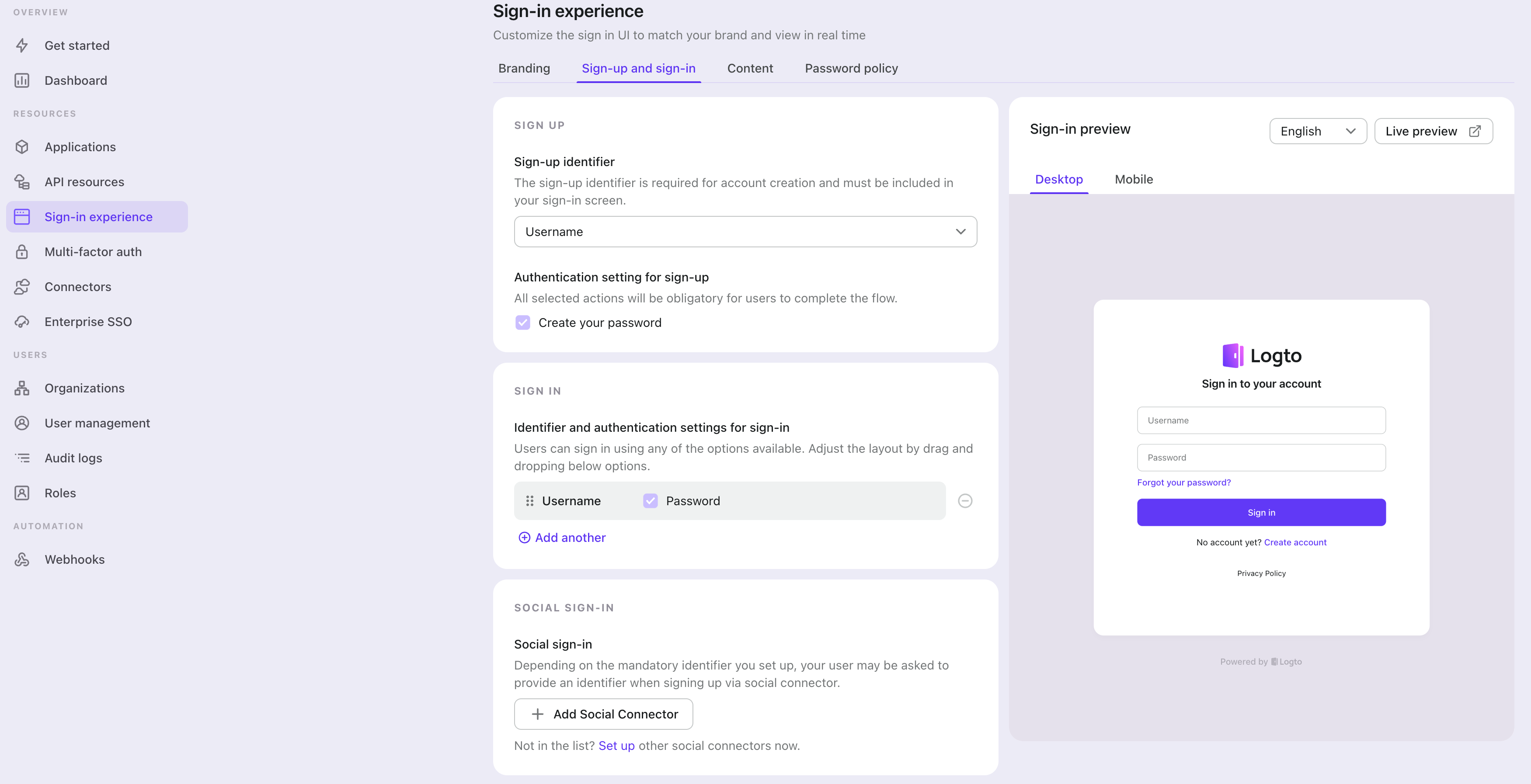
Select "None" for the "Sign-up identifier" to provide minimum sign-up effort for SAML sign-in, which may increase your conversion rate.
In the "Social sign-in" section, add "Add Social Connector" and choose "SAML". Then you should be able to see a button with text "Continue with SAML" in the preview section.

Finally, click "Save changes" on the bottom right corner.
Testing and Validation
Return to your Python app. You should now be able to sign in with SAML. Enjoy!
Further readings
Protect your API For native and single page apps, you'll need to call one or more API endpoints to retrieve and update data.
Learn more about identifying who's who and keeping your API secure.
User management We know you care about user management and activities, as we also do.
Learn more about how to know your users and see the figures like DAU and MAU graphically.
Localization From one regional business to a global corporate, the willingness to offer the best user experience won't change.
You can change current language phrases or add a new language without friction.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.